Home Recording Studio & Equipment
How to Put Together a Bedroom Home Studio on a Budget
Ever wonder what it’s like recording your own songs? Years ago, when you could record anything with a basic recorder. Either Reel-to-Reel or Cassette Tapes. Today, in the digital world of audio, you can record with a computer and a software DAW (Digital Audio Workstation), and you can transform a small space in your bedroom into a bedroom recording studio in your own (or parents) home.
I will explain what you need and suggest a selection of audio equipment, such as: Of course, a computer, desk, audio interface, Digital Audio Workstation (DAW) software, microphones for instruments and voice including pop filters, headphones, and speaker monitors. Since you have a small budget, soundproofing your room will increase your budget to reduce the audio noise that will bounce off your walls.
What do you need to build a bedroom recording studio at home? I’ll give you a basic list, and explain more in depth, suggest affordable audio equipment and where to buy. Of course you can go to your music store, electronic store and anyplace that sells audio equipment. Keep in mind that some retailers sell the same item that costs more than you would buy online.
Do your research before buying.
Before you buy any equipment, do all your research, prices will be the same on the popular online music stores that sells audio equipment and some items will vary.
Basic audio equipment list:
Computer, Display Monitor & External Hard Drive
Digital Audio Workstation software (DAW)
Audio Interface
Microphones & Pop Filter
Headphones
Speaker Monitors
Cables for microphones, speakers, instruments & amplifier
Desk-depends on the size of your space
Chair-Normal chair, not expensive, but comfortable to sit for long period of time
Pens, Pencil, Notepad & Blank Sheet Music when an idea inspires you
Computer, Display Monitor & External Hard Drive:
The most important equipment you need to create, record and edit audio in any DAW software. In addition to computer, is the size of your hard drive (HD) to save your projects, school essays and adding additional software. Random Access Memory (RAM) that perform everyday tasks, as saving a file, loading software applications. The more RAM the computer it has, you can open one or more applications to manage multiple tasks faster by switching from editing a document, checking email, open a couple of web pages to search.
Let’s discuss hardware disk capacity and external hard drive:
A hardware drive lets you store software apps and saving files after editing to your laptop hard drive. Some companies will give you the option by selecting the size of your hard drive is called “Disk Capacity. Disk capacity is measured in either GB (gigabytes) or TB (Terabytes). In todays’ computer technology, this is usually the norm.
Common capacity disk drives for hard drives are, 256GB, 512GB, 1TB, 2TB, 5TB and more. Companies do offer larger capacity drives for individuals works on multiple projects using different software applications such as 2TB, 4TB, and 8TB for additional cost.
When you need to continue to work on your music recordings, save your files to an external hard drive for safe keeping. Always make a copy of the file you’re working onto an external hard drive after you work on a song.
Let’s take a worst-case scenario. You just completed a song you recorded, you saved it to your HD. All of a sudden, your PC or Laptop begins to heat up and shuts down. You try powering back up, unfortunately it will not turn on. Even though it may be the motherboard, not the HD, but how do you access the files?
ALWAYS BACK UP YOUR FILES ON ANY PROJECT WORKING ON TO AN EXTERNAL HARD DRIVE!!
You’ll thank yourself later
Digital Audio Workstation (DAW):
This is the beginning of using a DAW to record your songs or recording a single track. With many DAWs to choose, you need do your research as well. For example, if your laptop is Apple MacBook, you need to find a DAW that is compatible with your MacBook, including a Windows version.
Below is a list of DAWs to research:
Garage Band - Usually included on your MacBook or you can download the app for free trom the app store
Ableton Live - Most popular of DAWs, more popular across both music production and live performance
Logic Pro - Great value including lifetime of free updates, AU plugins only, VST not supported
Steinberg Cubase - Great for electronic music producers
FL Studio - Very intuitive for creating beats, great DAW for beginner beatmakers
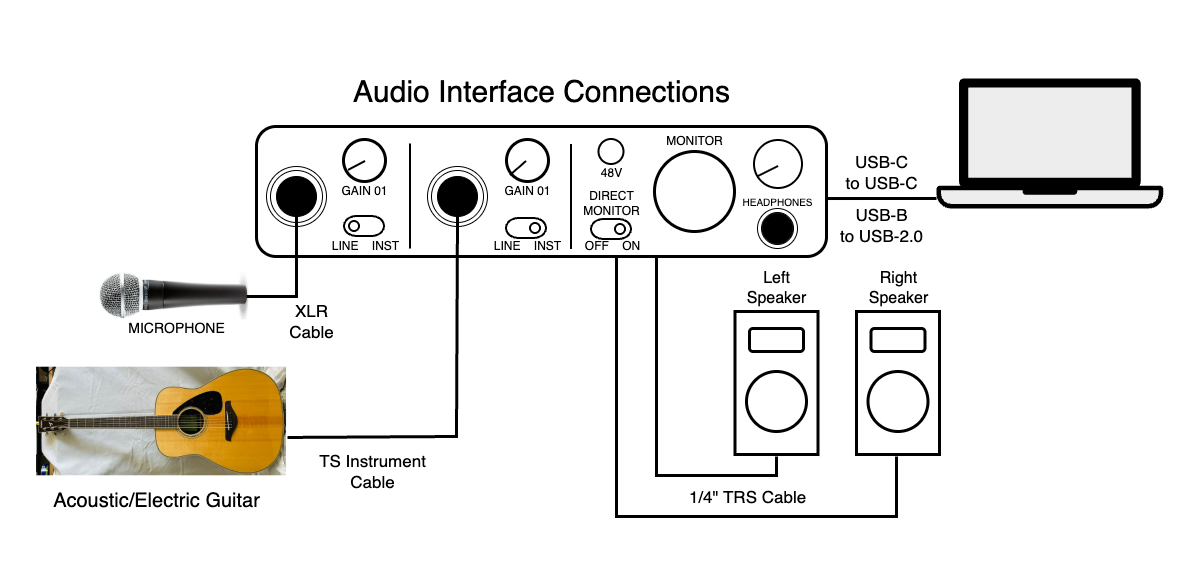
How Audio Interface Record Tracks into Your DAW:
An audio interface starts by receiving an analog signal from sound source, aka microphone, instruments or human voice and converts into a digital signal (1s & 0s). This process is analog-to-digital conversion.
The digital signal is transmitted to your computer by USB or Thunderbolt connection, into your DAW for recording and editing tracks.
The signal process is converted back from digital-to-analog and transmitted to speakers monitors or headphones to hear the sound you recorded.
A diagram below shows how an audio interface is connected to other audio equipment.
How Audio Interface Record Tracks into Your DAW:
An audio interface starts by receiving an analog signal from sound source, aka microphone, instruments or human voice and converts into a digital signal (1s & 0s). This process is analog-to-digital conversion.
The digital signal is transmitted to your computer by USB or Thunderbolt connection, into your DAW for recording and editing tracks.
The signal process is converted back from digital-to-analog and transmitted to speakers monitors or headphones to hear the sound you recorded.
Microphones and Pop Filters:
Microphone:
As your building up your bedroom studio, microphones are important piece of audio equipment you will encounter. A variety of microphones (mic) are used in the studio or onstage If you’re recording vocalist or instruments.
How does a microphone work?
Selecting a microphone to capture the sound source, either from an instrument or a vocalist singing. As the vocalist sings into the microphone, the diaphragm is set into motion and its movement creates an electrical current (waveform). The current or waveform is transmitted down a microphone cable into a various audio equipment that manipulate the sound or, an audio interface and coverts the analog current into a digital waveform that produces 1s and 0s.
Microphones are used in a variety of settings like concerts and recording studios. Microphones initially fall into three categories: dynamic (moving coil), ribbon, and condenser (capacitor).
Below are three explanations of each microphone and what is used for.
Dynamic: Moving Coil
It’s the most commonly used on a concert stage and small venues. The moving-coil microphone which a diaphragm is attached to a coil of wire which sits inside a magnet. When a sound source moves the diaphragm, it creates an electrical current within the magnetic field that creates an electrical waveform converts into an audio waveform. This dynamic microphone does not need external or phantom power.
Diagram of a Shure SM58 Cardioid Dynamic Microphone
Dynamic: Ribbon Microphone
A dynamic ribbon microphone function as the same as a dynamic moving coil microphone. The only difference it has a thin piece of corrugated metal ribbon suspended within a magnetic field. It takes the place of a moving coil and operates on the same as a moving coil. Also, the ribbon acts as both the diaphragm and to capture sound energy moving the ribbon which vibrates sympathetically. Like moving coils, ribbon coil microphones do not need external power supply or phantom power.
VERY IMPORTANT, ribbon coil microphones are very expensive to repair if damaged. Handle these mics with care.
Diagram of a Royer R-121 Ribbon Microphone.
Condenser/Capacitor Microphone:
Condenser microphones always require some electrical power, called in the form of +48V phantom power that is supplied from a studio console, mixer or an audio interface. A condenser uses a capacitor is made up with two (2) metal plates (one plate is positive (+) and the other plate a negative (-)), spaced apart, that can briefly hold an electrical charge. These plates are powered by +48V phantom power and also powers the internal preamp in the microphone.
When a vocalist sings into a condenser microphone, the diaphragm vibrates these plates that creates a variation of electrical voltage, then it’s transmitted through the microphone cable into the audio interface and sent to your DAW to display as an audio waveform.
Diagram of a MXL 990 Condenser/Capacitor Microphone.
Pop Filters:
Generally, a pop filter reduces popping sounds from plosive letters like “P” and “B” by diffusing the sound pressure or air blast from a vocalist before the sound enters the microphone and creates a cleaner vocal recording. Pop filters is a noise protection for microphone from loud plosive sounds (fast-moving air) and saliva during recorded singing, which can cause damage over time.
Diagram of a Proline PPF4012 Professional Pop Filter
Studio Headphones for Recording:
Studio Headphones are primarily used for musicians and vocalist for recording and listening during or after recording multiple tracks. It is also used for monitoring and production in professional studio environments for recording instruments and vocalist (tracking).
Why do musicians and vocalist wear headphones during recording? One reason while recording and listen accurately to backing tracks that was previously recorded tracks and to keep tempo while recording. Including tracking their own performance without interference aka “sound bleeding”.
What is sound bleeding?
Headphone bleed:
Sound escaping from headphones and being picked up by a microphone, particularly common when a vocalist sings along to a backing track.
Microphone crossover:
A microphone picks up the sound of another instrument or voice in the room. For example, a guitar amplifier mic picks up the sound of the drums.
Difference Between Closed-Back and Open-Back Headphones:
There is a difference between open-back vs closed-back headphones are used for a variety of reasons. Here are a few:
Closed-Back Headphones: Closed-back headphones to prevent sound from leaking in or out a recording. Also used to blocking external noise instruments from being heard by musicians and background vocalists.
Open-Back Headphones: Open-back headphones are designed to allow air and sound to pass through to provide a more natural and balanced soundstage or airy presence during recording.
Live sound bleed: Is when a live performance, or a microphone for one instrument (like a guitar) picks up unwanted sound from other instruments on stage (like drums).
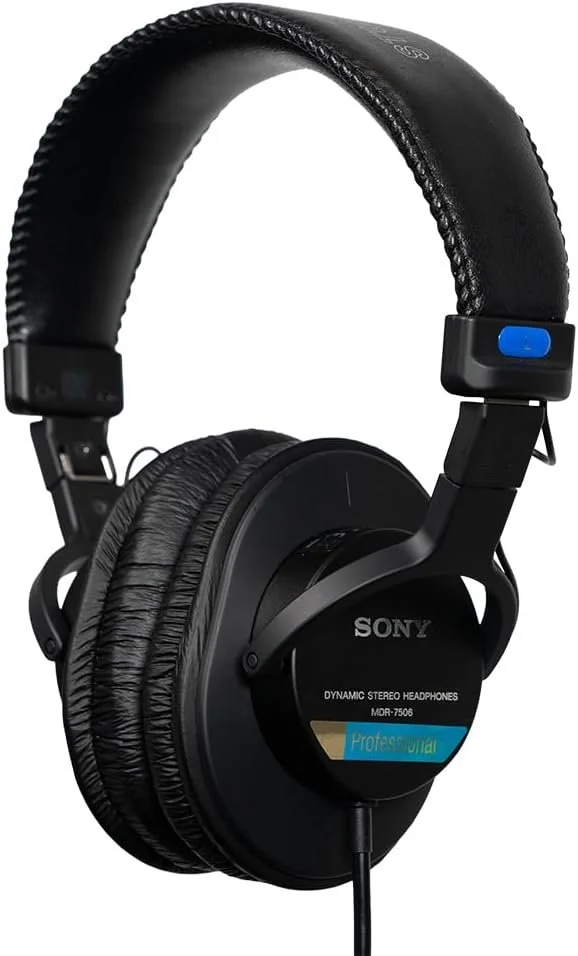
Diagram of a Sony MDR-7506 Closed-Back Studio Headphone
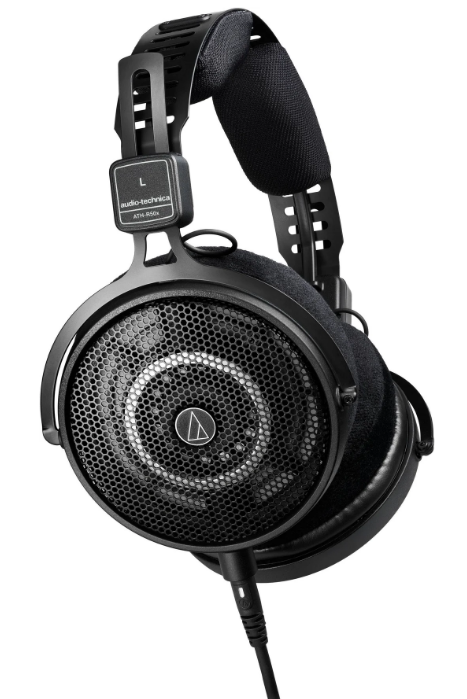
Diagram of an Audio-Technica ATH-R50X Open-Back Ref. Headphone
When you start to learn how to record and edit in your DAW, you will accurately monitor and edit your tracks effectively using headphones and to capture the sound you wanted to create. To eliminate any unwelcome sounds from your recording by editing accurately and listening after you edit each track to your satisfaction as a final product.
Studio Monitors:
When you start out building up your bedroom studio, if your budget allows for you to buy a decent size of 4in or 5in studio monitors in the range between.
What to Look for in Studio Monitors
Whether you’re starting out in audio/video production or upgrading your existing studio setup, the right monitors give you a true reflection of where your audio stacks up (and where it needs work). Before you purchase, you may want to consider the following factors:
Driver Size: For larger rooms, or if you’re addicted to bass, larger (8-inch and above) woofer cones are what you’re after. For smaller rooms, you’ll get away with smaller driver sizes—like these Adam T5Vs— which also means you save money.
Active vs Passive: If you’re running a dedicated amplifier, you can save money by purchasing passive speakers, which provide no amplification or EQ. Active speakers are powered and have their own amplifiers built in, so you can connect via a range of wired and wireless input options without requiring a separate amplifier.
Frequency Range: A wide frequency range means your monitors can accurately reproduce a wide spectrum of sound, from booming bass to trilling trebles, which they flatten out so all tones get the same level of amplification. A good starting point is around 50Hz–20kHz for most home producers.
Power Output: Again, your room size comes into play here. Lower outputs can still produce superb flat frequency response at lower volumes, like these 60W JBL desktop monitors. For the maximizers, these Focal Shape 65s pack a whopping 220W output (and a whopping price tag to match).
Equalization (EQ): Some monitors provide built-in EQ, which you can adjust via physical knobs and displays, or by using supplementary apps (or a combination of both). Options (like these KRK ROKIT 5s) come with preset modes to optimize levels for casual listening or hardcore production.
Decent studio monitors give users an unbiased reproduction of audio, so you can iron out any inconsistencies before your beloved tracks, videos, or podcast episodes before you distribute your audio or video recordings to the world. If you still haven’t found the right studio monitors for you, browse more top-rated options below.
Cables for Microphones, Speakers, Instrument & Amplifiers
Audio cables are essentials connecting audio equipment and instruments to send audio signals to your DAW.
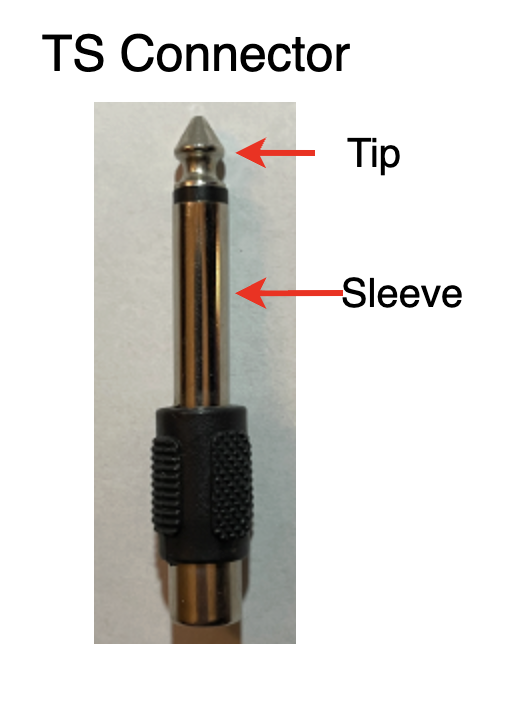
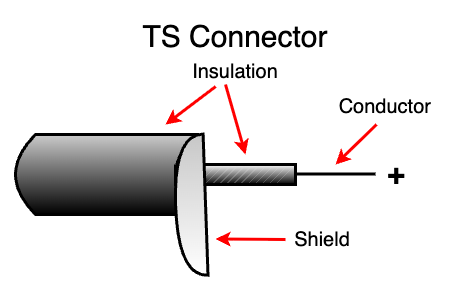
TS Connector Cable (Unbalanced):
TS (Tip-Sleeve) connectors are used mono unbalanced audio signals, primarily used for electric guitar connected to an amplifier.
Diagram of a TS Instrument Connector
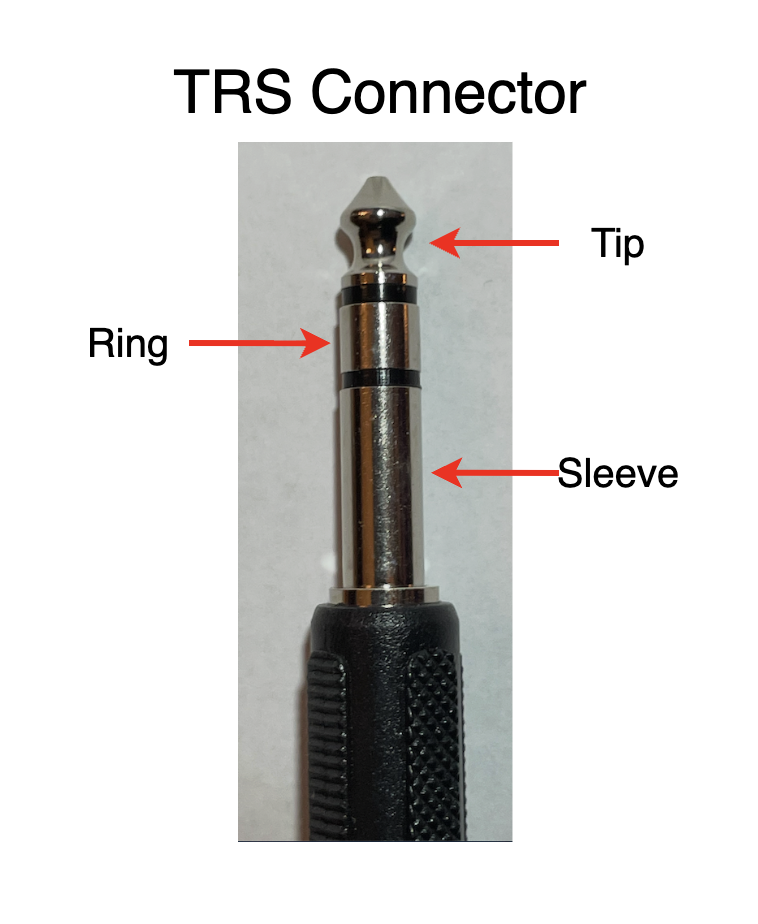
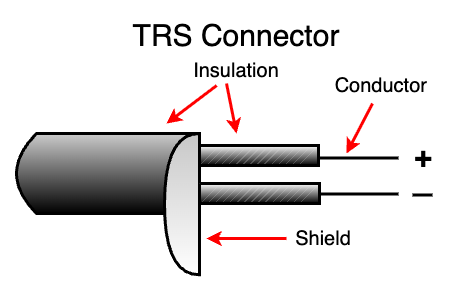
TRS Connector Cable (Balanced):
TRS (Tip-Ring-Sleeve) connector primarily used for sending balanced audio signals to left and right channels to a single cable that reduces humming and noise.
Diagram of a TRS Instrument Cable
Chair:
An office chair is your best bet to sit for long period of time and weight limit is about 200 lbs. If you like to play a guitar, make sure the arms of the chair can be removed. The last thing you want to do is to ding up your guitar while sitting with arms on each side that will get in the way of playing.
Pens, Pencil, Notepad & Blank Sheet Music (eraser):
Have you ever had an idea to write lyrics for a song? How about playing some guitar chords for a melody? When creativity strikes, you want to be prepared to write it all down, or ready to record by a stroke of a click.
Either way, you need a pen, pencil, notepad or blank sheet music to write. It can be a few chords, a couple of lines of lyrics or anything that demands your attention to write. Because, there were countless times I had an idea and lost it because I didn’t have anything to write.
If you have a smart phone, absolutely record those lyrics or hum that melody. When you get back to your home studio desk, you can take your creativity one step further and writing all down so it’s still inside you.
1. BlankSheetMusic.net: https://www.blanksheetmusic.net/
2. JustinGuitar.com: https://www.justinguitar.com/ This site is great for beginners.
3. JustinGuitar.com > Courses: Free courses for Beginners, Intermediate and one for Advanced
4. JustinGuitar.com: Most of my lessons are free! Please, consider donating and help keep it that way! :) Learn More: https://www.justinguitar.com/donate
5. Online Metronome: https://www.imusic-school.com/en/tools/online-metronome/
6. Online Metronome: Guitar App - https://guitarapp.com/metronome.html?tempo=113&timeSignature=2&pattern=1
7. Drummers Pulse: https://drummers-pulse.cerdmann.com/
8. The 80/20 rule means that 80% of your progress comes from just 20% of what you practice.
9. Mussica: https://www.musicca.com/metronome
10. Unlock the Guitar > Blank Fretboard Diagram – Jazz Guitar Licks: https://www.jazz-guitar-licks.com/pages/tools-for-musicians/printable-blank-guitar-fretboard-diagrams.html
11. Jazz Guitar Lessons: https://www.jazz-guitar-licks.com/pages/tools-for-musicians/printable-blank-guitar-fretboard-diagrams.html
12. Musescore: The most worlds notation app. Download for free at: https://musescore.org/en
JustinGuitar.com:
Sharing his passion for music has always been important to him! JustinGuitar.com went live back in July 2003 to support his private lessons. He moved to free digital lessons on YouTube in 2006, before almost anyone else was teaching there. The response was so inspiring! It helped him realize his mission: to provide the best guitar education to everyone, no matter their circumstances.
Millions of people around the world learn to play with JustinGuitar.com. He developed practical courses that will help you learn quickly and stay motivated. He always believed that everyone should have access to high-quality guitar education, and that's why he runs the site on donations instead of paywalls!
He carefully designs his courses to help students make the best out of their guitar time! His lessons feel like private lessons and are just as effective. The best part? They're open to everyone.
Courses:
Free Courses by Justin Sandercoe
Beginner Grade 1, 2, 3
In his lessons, he will teach you the basics of a guitar parts, playing chords, Basic Theory & Strumming Development, learning a scale, and many more lessons to get you started on the right path to playing your guitar correctly.
Review these 3 courses, take notes and write a summary of these courses how it can benefit a beginner guitar player.
JustinGuitar.com has lessons for Left Handed Beginner Guitar Players. Include links to JustinGuitar.com
Mussica.com
Musicca.com was founded in Denmark in 2019 by Lasse Grubbe, who holds a Master of Arts in Musicology. He created Musicca.com so that everyone can have the opportunity to learn music theory. For free, forever.
Today, Musicca.com is a global learning platform for students, educators, and musicians around the world. With several million monthly users in more than 150 countries, Musicca.com is one of the most popular music learning platforms in the world.
Musicca.com provides interactive exercises, tools and resources that encourage musicians and students to improve their musical skills, both in school and at home. We focus on skills that are essential for reading, writing and playing music.
Musicca.com makes learning music fun by adding game elements to the learning process. Learning is easier and more effective when you're having fun. Musicca.com can be used anywhere, using any device with an internet connection.
His team comprises talented people from diverse backgrounds. We are copywriters, developers, designers, teachers, musicians, and translators who are passionate about providing more people with the opportunity to learn music.
If you like to see who have helped create the content and website, please click here on their website, Musicca.com.
Blank Sheet Music (free):
Blank Sheet Music is a free resource site that provides free printable blank sheet music for inspiring students, musicians and songwriters.
Click on Blank Sheet Music and view their website
BlankSheetMusic.net: https://www.blanksheetmusic.net/
Staff Paper Archive: https://www.blanksheetmusic.net/staff_paper#google_vignette
Jazz Guitar Lessons:
Stef Ramin
https://www.jazz-guitar-licks.com/members/profile/stef-jazz-guitar-licks/
Blog and Free Lessons, tons of Learning Materials, PDF Methods, Backing Tracks to play along.